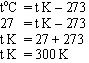1. Suhu suatu zat menyatakan ...
a. jumlah molekul zat
b. tingkat kenaikan volume zat
c. tingkat panas atau dinginnya suatu zat
d. tingkat pemuaian zat
pembahasan :
suhu atau temperatur adalah besaran yang menyatakan derajat (tingkat) panas atau dinginnya suatu zat
jawaban : c
2. Satuan Internasional (SI) yang digunakan untuk suhu adalah ...
a. celcius b. fahrenheit
c. reamur d. kelvin
pembahasan :
satuan internasional (SI) untuk suhu adalah kelvin karena dalam banyak pengukuran di bidang riset khususnya dalam bidang riset temperatur rendah satuan celcius, reamur, dan fahrenheit menggunakan angka nol dan minus dalam nilai temperatur sehingga menyulitkan perhitungan secara matematis, sehingga ditetapkan bahwa suhu terendah adalah 0 kelvin
jawaban : d
3. Suhu suatu zat diukur dengan ...
a. barometer b. termometer
c. higrometer d. manometer
pembahasan :
- barometer adalah alat untuk mengukur tekanan udara luar
- termometer adalah alat untuk mengukur suhu
- higrometer adalah alat untuk mengukur kelembapan udara
- manometer adalah alat untuk mengukur tekanan udara dalam ruang tertutup
jawaban : b
4. Pernyataan berikut ini benar, kecuali ...
a. suhu merupakan besaran turunan
b. alat ukur suhu adalah termometer
c. suhu menyatakan derajat panas sebuah benda
d. molekul-molekul sebuah benda bergetar cepat jika suhu dinaikkan
pembahasan :
suhu merupakan salah satu besaran pokok
jawaban : a
5. Air tidak dipakai untuk mengisi termometer. Hal ini karena ...
a. volume air tetap
b. tidak memuai ketika dipanaskan
c. memiliki pemuaian yang kecil
d. air membasahi dinding
pembahasan :
alasan mengapa air tidak digunakan untuk mengisi tabung termometer antara lain :
- air membasahi dinding
- tidak berwarna
- jangkauan suhu air terbatas (0 - 100) derajat C
- perubahan volume air sangat kecil ketika suhunya dinaikkan
- merupakan penghantar panas yang sangat jelek
jawaban : d
6. Salah satu keuntungan alkohol sebagai pengisi termometer adalah ...
a. dapat mengukur suhu yang sangat tinggi
b. dapat mengukur suhu yang sangat rendah
c. tidak berwarna
d. tidak membasahi dinding tabung
pembahasan :
keuntungan alkohol sebagai termometer :
- alkohol sangat murah dibanding raksa
- dapat mengukur suhu dengan sangat teliti
- dapat mengukur suhu yang sangat rendah
jawaban : b
7. Keuntungan raksa sebagai pengisi termometer adalah :
(1) tidak membasahi dinding
(2) pemuaiannya tidak teratur
(3) mudah dilihat
(4) titik bekunya rendah
Pernyataan di atas yang benar adalah ...
a. 1, 2, dan 3 b. 1 dan 3
c. 2 dan 4 d. 4 saja
Pembahasan :
keuntungan raksa sebagai pengisi termometer sebagai berikut :
(1) mudah dilihat
(2) tidak membasahi dinding
(3) jangkauan suhu cukup lebar (-40 sampai 350 derajat C)
(4) merupakan penghantar panas yang baik
jawaban : b
8. Titik tetap atas termometer celcius adalah ...
a. suhu es yang mencair
b. suhu air yang membeku
c. suhu air yang panas
d. suhu air yang mendidih
pembahasan :
titik tetap atas termometer celcius adalah suhu didih air, sedangkan titik tetap bawah adalah suhu lebur air
jawaban : d
9. Termometer klinis mempunyai daerah ukur antara ...
a. (0 - 50) derajat C b. (0 - 100) derajat C
c. (30 - 40) derajat C d. (35 - 42) derajat C
pembahasan :
termometer klinis digunakan untuk mengukur suhu tubuh. Karena suhu terendah manusia tidak pernah kurang dari 35 derajat C dan suhu tertinggi tidak pernah lebih dari 42 derajat C, maka angka-angka pada skala didesain antara 35 - 42 derajat C
jawaban : d
10. Pada termometer celcius, titik didih air adalah 100 derajat C. Pada termometer fahrenheit nilai ini sama dengan ...
a. 212 derajat F b. 180 derajat F
c. 132 derajat F d. 32 derajat F
pembahasan :
pada skala fahrenheit, titik didih air adalah 212 derajat C, atau dapat juga dihitung dari rumus konversi skala celcius ke skala fahrenheit sebagai berikut :
dari soal diketahui t derajat C = 100 derajat C, maka :
jawaban : a
11. Suhu suatu zat adalah 25 derajat C. Jika diukur oleh termometer skala fahrenheit, maka suhu zat tersebut adalah ...
a. 97 derajat F b. 95 derajat F
c. 77 derajat F d. 45 derajat F
pembahasan :
dari soal diketahui :
t derajat C = 25
maka :
jawaban : c
12. Suhu suatu zat diukur oleh termometer reamur adalah 60 derajat. Bila diukur oleh termometer celcius adalah ...
a. 28 derajat b. 48 derajat
c. 75 derajat d. 80 derajat
pembahasan :
dari soal diketahui t derajat R = 60 derajat
maka :
jawaban : c
13. Titik didih air di permukaan laut adalah ... derajat C.
a. 76 b. 78 c. 98 d. 100
pembahasan :
titik didih air pada tekanan 76 cmHg (tekanan udara di permukaan laut) adalah 100 derajat C
jawaban : d
14. Titik tetap bawah termometer celcius dibuat dengan cara mencelupkan reservoirnya ke dalam ...
a. larutan garam
b. es yang sedang melebur
c. campuran es dan garam
d. air yang sedang mendidih
pembahasan :
pada termometer celcius, titik tetap bawah adalah es yang sedang melebur (titik lebur es) dan titik tetap atas adalah air yang sedang mendidih (titik didih air)
jawaban : b
15. Termometer fahrenheit menunjukkan angka yang sama dengan dua kali angka yang ditunjukkan oleh termometer celcius pada suhu ...
a. 20 derajat C b. 40 derajat C
c. 80 derajat C d. 160 derajat C
pembahasan :
misalkan t derajat C = y, dari soal diketahui
Baca Selengkapnya..
a. jumlah molekul zat
b. tingkat kenaikan volume zat
c. tingkat panas atau dinginnya suatu zat
d. tingkat pemuaian zat
pembahasan :
suhu atau temperatur adalah besaran yang menyatakan derajat (tingkat) panas atau dinginnya suatu zat
jawaban : c
2. Satuan Internasional (SI) yang digunakan untuk suhu adalah ...
a. celcius b. fahrenheit
c. reamur d. kelvin
pembahasan :
satuan internasional (SI) untuk suhu adalah kelvin karena dalam banyak pengukuran di bidang riset khususnya dalam bidang riset temperatur rendah satuan celcius, reamur, dan fahrenheit menggunakan angka nol dan minus dalam nilai temperatur sehingga menyulitkan perhitungan secara matematis, sehingga ditetapkan bahwa suhu terendah adalah 0 kelvin
jawaban : d
3. Suhu suatu zat diukur dengan ...
a. barometer b. termometer
c. higrometer d. manometer
pembahasan :
- barometer adalah alat untuk mengukur tekanan udara luar
- termometer adalah alat untuk mengukur suhu
- higrometer adalah alat untuk mengukur kelembapan udara
- manometer adalah alat untuk mengukur tekanan udara dalam ruang tertutup
jawaban : b
4. Pernyataan berikut ini benar, kecuali ...
a. suhu merupakan besaran turunan
b. alat ukur suhu adalah termometer
c. suhu menyatakan derajat panas sebuah benda
d. molekul-molekul sebuah benda bergetar cepat jika suhu dinaikkan
pembahasan :
suhu merupakan salah satu besaran pokok
jawaban : a
5. Air tidak dipakai untuk mengisi termometer. Hal ini karena ...
a. volume air tetap
b. tidak memuai ketika dipanaskan
c. memiliki pemuaian yang kecil
d. air membasahi dinding
pembahasan :
alasan mengapa air tidak digunakan untuk mengisi tabung termometer antara lain :
- air membasahi dinding
- tidak berwarna
- jangkauan suhu air terbatas (0 - 100) derajat C
- perubahan volume air sangat kecil ketika suhunya dinaikkan
- merupakan penghantar panas yang sangat jelek
jawaban : d
6. Salah satu keuntungan alkohol sebagai pengisi termometer adalah ...
a. dapat mengukur suhu yang sangat tinggi
b. dapat mengukur suhu yang sangat rendah
c. tidak berwarna
d. tidak membasahi dinding tabung
pembahasan :
keuntungan alkohol sebagai termometer :
- alkohol sangat murah dibanding raksa
- dapat mengukur suhu dengan sangat teliti
- dapat mengukur suhu yang sangat rendah
jawaban : b
7. Keuntungan raksa sebagai pengisi termometer adalah :
(1) tidak membasahi dinding
(2) pemuaiannya tidak teratur
(3) mudah dilihat
(4) titik bekunya rendah
Pernyataan di atas yang benar adalah ...
a. 1, 2, dan 3 b. 1 dan 3
c. 2 dan 4 d. 4 saja
Pembahasan :
keuntungan raksa sebagai pengisi termometer sebagai berikut :
(1) mudah dilihat
(2) tidak membasahi dinding
(3) jangkauan suhu cukup lebar (-40 sampai 350 derajat C)
(4) merupakan penghantar panas yang baik
jawaban : b
8. Titik tetap atas termometer celcius adalah ...
a. suhu es yang mencair
b. suhu air yang membeku
c. suhu air yang panas
d. suhu air yang mendidih
pembahasan :
titik tetap atas termometer celcius adalah suhu didih air, sedangkan titik tetap bawah adalah suhu lebur air
jawaban : d
9. Termometer klinis mempunyai daerah ukur antara ...
a. (0 - 50) derajat C b. (0 - 100) derajat C
c. (30 - 40) derajat C d. (35 - 42) derajat C
pembahasan :
termometer klinis digunakan untuk mengukur suhu tubuh. Karena suhu terendah manusia tidak pernah kurang dari 35 derajat C dan suhu tertinggi tidak pernah lebih dari 42 derajat C, maka angka-angka pada skala didesain antara 35 - 42 derajat C
jawaban : d
10. Pada termometer celcius, titik didih air adalah 100 derajat C. Pada termometer fahrenheit nilai ini sama dengan ...
a. 212 derajat F b. 180 derajat F
c. 132 derajat F d. 32 derajat F
pembahasan :
pada skala fahrenheit, titik didih air adalah 212 derajat C, atau dapat juga dihitung dari rumus konversi skala celcius ke skala fahrenheit sebagai berikut :
dari soal diketahui t derajat C = 100 derajat C, maka :
jawaban : a
11. Suhu suatu zat adalah 25 derajat C. Jika diukur oleh termometer skala fahrenheit, maka suhu zat tersebut adalah ...
a. 97 derajat F b. 95 derajat F
c. 77 derajat F d. 45 derajat F
pembahasan :
dari soal diketahui :
t derajat C = 25
maka :
jawaban : c
12. Suhu suatu zat diukur oleh termometer reamur adalah 60 derajat. Bila diukur oleh termometer celcius adalah ...
a. 28 derajat b. 48 derajat
c. 75 derajat d. 80 derajat
pembahasan :
dari soal diketahui t derajat R = 60 derajat
maka :
jawaban : c
13. Titik didih air di permukaan laut adalah ... derajat C.
a. 76 b. 78 c. 98 d. 100
pembahasan :
titik didih air pada tekanan 76 cmHg (tekanan udara di permukaan laut) adalah 100 derajat C
jawaban : d
14. Titik tetap bawah termometer celcius dibuat dengan cara mencelupkan reservoirnya ke dalam ...
a. larutan garam
b. es yang sedang melebur
c. campuran es dan garam
d. air yang sedang mendidih
pembahasan :
pada termometer celcius, titik tetap bawah adalah es yang sedang melebur (titik lebur es) dan titik tetap atas adalah air yang sedang mendidih (titik didih air)
jawaban : b
15. Termometer fahrenheit menunjukkan angka yang sama dengan dua kali angka yang ditunjukkan oleh termometer celcius pada suhu ...
a. 20 derajat C b. 40 derajat C
c. 80 derajat C d. 160 derajat C
pembahasan :
maka
jawaban : d
16. Suhu suatu zat menurut termometer celcius adalah 27 derajat C, maka menurut kelvin suhu itu sama dengan ...
a. 27 K b. 127 K c. 300 K d. 400 K
pembahasan :
dari soal diketahui
maka
jawaban : c
17. Penunjukan skala termometer berikut yang mempunyai suhu paling rendah adalah ...
a. 0 K b. 0 derajat C c. 0 derajat R d. 0 derajat F
pembahasan :
untuk mengetahui suhu yang paling rendah, maka skala suhu tersebut kita ubah ke skala celcius, maka :
(1) kelvin ke celcius
(2) reamur ke celcius
(3) fahreheit ke celcius
dengan demikian, suhu terendah adalah - 273 derajat C = 0 K
jawaban : a
18. Suhu suatu zat diukur oleh termometer fahrenheit adalah 55 derajat F. Jika diukur dengan termometer kelvin, maka suhu zat tersebut sebesar ...
a. 285,8 K b. 385,8 K c. 485,8 K d. 585,8 K
pembahasan :
dari soal diketahui :
maka kita cari dulu t derajat C :
dari rumus
jawaban : a
19. Suatu zat memiliki suhu sebesar 333 K, jika diukur dengan menggunakan termometer skala fahrenheit, maka suhu zat tersebut sebesar ...
a. 140 derajat F b. 150 derajat F
c. 160 derajat F d. 170 derajat F
pembahasan :
dari soal diketahui t K = 333
jawaban : a
20. Sebagai titik patokan atas pada termometer fahrenheit adalah ...
a. suhu es yang sedang mencair
b. suhu es yang sedang mendidih
c. suhu badan orang sehat
d. campuran es dengan garam
pembahasan :
termometer fahrenheit memiliki ciri-ciri :
1. menggunakan air raksa sebagai pengisi termometer
2. patokan bawah (titik 0 derajat F) adalah suhu campuran es dan garam yang sedang mencair
3. patokan atas (titik 96 derajat F) adalah suhu tubuh orang sehat
jawaban : c
21. Sebagai titik awal pengukuran suhu badan manusia pada termometer klinik diambil suhu terendah badan manusia, yaitu ...
a. 25 derajat C
b. 27 derajat C
c. 35 derajat C
d. 42 derajat C
pembahasan :
suhu tubuh manusia memiliki titik terendah sebesar 35 derajat C dan suhu tertinggi 42 derajat C
jawaban : c
22. Alat untuk menyelidiki pemuaian berbagai zat padat adalah ...
a. barometer
b. bimetal
c. termometer
d. musschenbroek
pembahasan :
1. termometer adalah alat untuk mengukur tekanan udara luar
2. bimetal adalah dua keping logam yang angka muainya berbeda dikeling menjadi satu
3. termometer adalah alat untuk mengukur suhu
4. musschenbroek adalah alat untuk menyelidiki pemuaian berbagai zat padat
jawaban : d
23. Batang besi panjangnya 2 m pada suhu 20 derajat C. Setelah suhunya mencapai 80 derajat C, panjang batang besi menjadi ... (α = 0,000011/oC)
a. 2,0013 m
b. 2,0126 m
c. 2,0168 m
d. 2,0260 m
pembahasan :
Dari soal diketahui lo = 2 m
to = 20oC
t = 80oC
α = 0,000011/oC
maka :
Δt = t - to
= 80oC – 20oC
= 60oC
Dan l = lo {1
+ α Δt}
=
2 {1 + (0,000011)(60)}
= 2 (1 + 0,000660)
= 2 (1,000660) = 2,00132 m
jawaban : A
24. Pada suhu 25 derajat C, panjang batang besi adalah 2 m. Berapakah panjang batang besi itu pada suhu 40 derajat C ? Jika :

jawaban : A
24. Pada suhu 25 derajat C, panjang batang besi adalah 2 m. Berapakah panjang batang besi itu pada suhu 40 derajat C ? Jika :
a. 2,000 m
b. 2,00055 m
c. 2,0033 m
d. 0,0033 m
pembahasan :
dari soal diketahui :
maka :
jawaban : C
25. Apabila koefisien muai panjang suatu logam adalah :
pembahasan :
koefisien muai volume suatu zat padat adalah tiga kali koefisien muai panjangnya. Dengan demikian :
jawaban : d
26. Koefisien muai panjang suatu zat padat bergantung pada ...
a. panjang batang mula-mula
b. jenis zat padat
c. perubahan suhu
d. pertambahan panjang
pembahasan :
koefisien muai panjang berbagai zat padat diselidiki oleh alat yang disebut musschenbroek. Ternyata, untuk panjang yang sama dan perubahan suhu yang sama, pertambahan panjang berbagai zat padat berbeda-beda. Ini menunjukkan bahwa koefisien muai panjang suatu zat berbeda-beda, bergantung pada jenis zat padat.
jawaban : b
27. Angka muai gas besarnya sama dengan ...
pembahasan :
angka muai setiap jenis gas, menurut hasil pengamatan Gay Lussac, ternyata sama yaitu sebesar
jawaban : a
28. Volume minyak tanah dalam sebuah wadah pada suhu 0 derajat C adalah 1 liter. JIka koefisien muai ruang minyak tanah  , maka volume minyak tanah pada suhu 100 derajat C adalah ...
, maka volume minyak tanah pada suhu 100 derajat C adalah ...
a. 1,000955 liter
b. 1,00955 liter
c. 1,0955 liter
d. 1,955 liter
pembahasan :
dari soal diketahui :
maka :
jawaban : c
29. Sebuah keping bimetal terbuat dari logam kuningan dan besi. Jika angka muai panjang kuningan lebih besar daripada besi, maka ketika bimetal dipanaskan ...
a. membengkok ke arah besi
b. membengkok ke arah kuningan
c. tetap lurus
d. menyusut
pembahasan :
jika keping bimetal dipanaskan, maka bimetal tersebut akan membengkok ke arah logam yang koefisien muainya terkecil. Karena kuningan memiliki koefisien muai panjang lebih besar daripada besi, maka bimetal akan membengkok ke arah besi
jawaban : a
30. Berikut adalah cara mengatasi masalah yang ditimbulkan oleh pemuaian, kecuali ...
a. membuat celah pada sambungan rel kereta api
b. membuat celah pada sambungan jembatan
c. membuat keping bimetal pada saklar otomatis
d. membuat ukuran bingkai jendela lebih besar dari kacanya
pembahasan :
pada siang hari, ketika panas terik, semua zat akan memuai. Seandainya sambungan rel atau jembatan tidak diberi celah, maka rel atau jembatan akan melengkung. Demikian, pula pada pemasangan kaca jendela. Apabila bingkai tepat sama dengan ukuran kacanya, maka tidak ada ruang tambahan ketika memuai. Ini akan mengakibatkan kaca retak. Sementara itu, membuat keping bimetal pada saklar otomatis tidak termasuk mengatasi masalah yang ditimbulkan oleh pemuaian, tetapi justru memanfaatkan peristiwa pemuaian
jawaban : c
31. Jika suatu zat dipanaskan sehingga mengalami kenaikan suhu 1 derajat C, maka zat yang memuai terbesar adalah ...
a. zat padat
b. zat cair
c. gas
d. tidak dapat ditentukan
pembahasan :
untuk kenaikan suhu yang sama, pemuaian suatu zat bergantung pada volume mula-mula dan koefisien muai ruang zat tersebut. Karena tidak diketahui volume zat mula-mula, maka pemuaian zat tersebut tidak dapat ditentukan
jawaban : d
32. Berikut ini pemanfaatan pemuaian dalam kehidupan sehari-hari, kecuali ...
a. pemasangan jembatan besi
b. pengelingan pelat logam
c. memasang roda pada ban baja sebuah lokomotif
d. keping bimetal
pembahasan :
pemanfaatan pemuaian dalam kehidupan sehari-hari antara lain :
- pengelingan pelat logam
- keping bimetal
- memasang roda pada ban baja sebuah lokomotif
jawaban : a
33. Alat yang tidak memanfaatkan bimetal adalah ...
a. termometer
b. saklar lampu
c. termostat
d. lampu tanda arah mobil
pembahasan :
termometer, secara umum tidak memanfaatkan bimetal, tetapi mempergunakan zat cair sebagai penigisi tabung termometer
jawaban : a
34. Supaya kaca pada filamen lampu pijar tidak pecah ketika dinyalakan, maka harus dibuat dari bahan gelas yang mempunyai ...
a. koefisien muai ruang besar
b. koefisen muai ruang kecil
c. massa jenis besar
d. massa jenis kecil
pembahasan :
pada saat lampu pijar menyala maka lampu akan panas. Udara yang berada dalam lampu akan memuai. Agar kaca tidak pecah karena pemuaian gas, maka kaca harus memiliki koefisien muai ruang yang besar
jawaban : a
35. Pemasangan kawat jaringan listrik tidak terlalu tegang. Hal ini dilakukan agar ...
a. tidak putus ketika panas
b. tidak putus ketika dingin
c. melengkung ketika panas
d. ada kesempatan pemuaian
pembahasan :
kawat jaringan listrik atau telepon dibiarkan kendor ketika panas. ini bertujuan agar ketika dingin, penyusutan kawat tidak mengakibatkan tali putus karena terlalu tegang
jawaban : b